Hybrid decentralized trials have become a key consideration for sponsors evaluating how to balance participant convenience with operational and regulatory requirements as clinical research continues to evolve beyond fully site-based execution. Advances in digital tools, remote data capture, and home-based services have expanded how studies can be designed, while regulatory expectations continue to emphasize oversight, documentation, and participant safety.
For sponsors, the challenge is not whether to adopt decentralized elements, but how to apply them appropriately within each protocol. This guide provides a practical comparison of hybrid and fully decentralized trial models, helping sponsors assess structure, feasibility, and operational fit when planning studies.
What Are Hybrid Decentralized Trials?
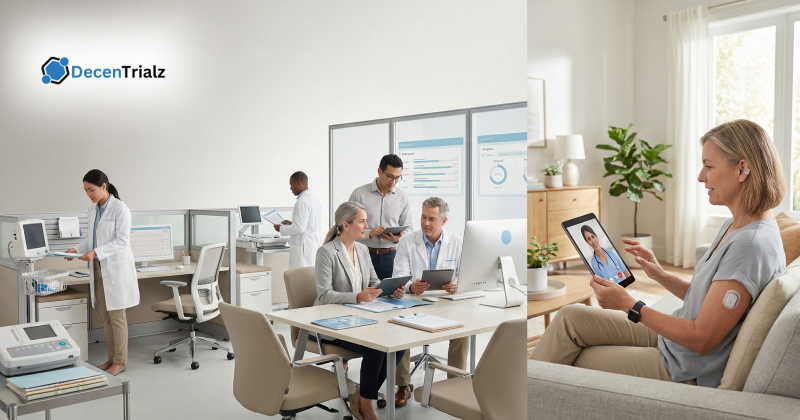
Hybrid decentralized trials combine traditional site-based activities with remote and digital components within a single study design. In this model, core clinical activities such as physical examinations, investigational product administration, or complex assessments continue to occur at research sites, while other interactions are conducted remotely.
Hybrid clinical trials often include telehealth visits, electronic consent, wearable data collection, home nursing services, and centralized digital platforms. This approach allows sponsors to maintain investigator oversight and regulatory alignment while reducing participant burden and improving accessibility.
Hybrid decentralized trials are commonly selected when full decentralization is not feasible due to safety, protocol complexity, or regulatory considerations, but where remote elements can improve operational efficiency and participant experience.
What Are Fully Decentralized Clinical Trials?
Fully decentralized clinical trials are designed to operate without routine on-site visits. Study activities are conducted through digital platforms, home-based services, and remote coordination, allowing participants to take part without traveling to research sites.
In decentralized clinical trials, screening, consent, monitoring, and data collection rely on telemedicine, mobile health technologies, direct-to-participant logistics, and centralized coordination teams. These models can improve geographic reach, expand access to underrepresented populations, and reduce logistical barriers to participation.
However, fully decentralized trials require robust digital infrastructure, clearly defined workflows, and strong participant support to ensure protocol adherence, data quality, and safety oversight throughout the study lifecycle.
Key Differences Between Hybrid and Fully Decentralized Trials
Although both models incorporate decentralized capabilities, their operational structures differ in ways that significantly affect sponsor decision-making.
Hybrid decentralized trials retain defined site involvement, with investigators overseeing critical clinical elements while remote components supplement traditional visits. Fully decentralized trials, by contrast, minimize or eliminate routine site interactions and rely more heavily on centralized coordination and digital systems.
Participant interaction also differs between models. Hybrid approaches alternate between in-person and remote engagement, while fully decentralized trials rely almost entirely on virtual touchpoints. Operational oversight in hybrid designs is distributed across sites and centralized platforms, whereas fully decentralized trials depend on integrated digital workflows and vendor coordination.
Understanding how these clinical elements are distributed helps sponsors align trial design with operational capabilities and risk management strategies.
Decision Factors Sponsors Should Consider
Selecting between hybrid decentralized trials and fully decentralized models requires careful evaluation of study-specific factors.
Study indication plays a key role, as therapeutic areas requiring imaging, physical examinations, or complex interventions may necessitate site involvement. Participant population characteristics, including age, disease severity, and digital literacy, also influence whether remote participation is practical.
Geographic considerations may support decentralized elements when participants are widely distributed or face access barriers. Regulatory expectations across regions further shape which activities can be conducted remotely and how sponsor oversight must be maintained.
Addressing these factors early helps sponsors avoid protocol amendments, operational delays, and enrollment inefficiencies later in the study.
Operational Complexity and Oversight Considerations
Decentralized approaches introduce additional layers of coordination across sponsors, CROs, sites, vendors, and technology platforms. Sponsors must manage data flow from multiple sources, ensure consistency in protocol execution, and maintain visibility into study progress.
Remote monitoring supports centralized oversight by enabling review of safety data, protocol adherence, and operational performance. Clear role definitions, standardized procedures, and transparent reporting structures are essential to maintaining accountability across both hybrid decentralized trials and fully decentralized designs.
Effective oversight allows sponsors to preserve control while benefiting from the flexibility that decentralized elements provide.
Regulatory Considerations for Decentralized Trial Models
Regulatory authorities have acknowledged the role of decentralized approaches while reinforcing sponsor responsibility for participant safety and data integrity. Guidance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration emphasizes the importance of documentation, vendor oversight, validated technologies, and clear informed consent processes when decentralized components are used.
Sponsors should ensure that decentralized activities are clearly described in protocols, supported by compliant systems, and aligned with regional regulatory requirements. Maintaining audit trails and oversight mechanisms remains essential regardless of the trial model selected.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Study
There is no single model that fits all trials. Hybrid decentralized trials and fully decentralized designs represent strategic options that should be selected based on protocol needs, risk profiles, and operational readiness.
Sponsors may introduce virtual clinical trials components selectively, preserving site-based execution for critical activities while decentralizing interactions that do not require in-person oversight. This flexibility allows sponsors to balance efficiency, participant experience, and regulatory confidence across different development stages.
Enabling Early Alignment and Feasibility Clarity
Early alignment on eligibility criteria, participant expectations, and operational readiness significantly improves trial execution. When sponsors establish clarity upfront, they reduce downstream challenges related to screen failures, protocol deviations, and enrollment delays.
Using instant match approaches to align protocol requirements with participant characteristics supports more accurate feasibility planning, particularly when sponsors review trials organized by condition to understand early recruitment and eligibility alignment.
How DecenTrialz Supports Sponsors Through Structured Pre-Screening and Site Referral
DecenTrialz supports sponsors by strengthening the recruitment and pre-screening stage that occurs before trial execution begins. The platform focuses on organizing study requirements, guiding participants through early eligibility steps, and delivering site-ready referrals without influencing trial design, execution models, or operational decisions.
Study requirements are first organized into a clear, structured framework. Key protocol criteria are mapped into a format that guides the pre-screening process. Participants receive study information through a simple digital consent experience and complete guided pre-screening questions in a logical sequence to assess initial eligibility alignment.
A registered nurse then follows up to review responses, ask study-specific questions, and ensure participants understand expectations before moving forward. Only participants who meet the outlined requirements are referred to research sites, supporting a more prepared, informed, and organized handoff.
By improving early eligibility screening, participant understanding, and referral quality, DecenTrialz helps sponsors, CROs, and sites reduce screening inefficiencies and accelerate enrollment while maintaining clear boundaries between recruitment, site execution, and regulatory oversight.
Plan Hybrid and Decentralized Trials With Confidence
Sponsors looking to strengthen early feasibility and recruitment alignment can explore additional resources on the DecenTrialz page for sponsors, review insights shared on the DecenTrialz blog, or learn more about the platform’s approach through the DecenTrialz About Us page.